Uncovering the Impact of Helicobacter Pylori on Human Health

Guidelines for Testing for Pylori at Home
2023-02-15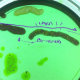
which are the current diagnostic measures on the Helicobacter Pylori affection?
2023-02-16Uncovering the Impact of Helicobacter Pylori on Human Health

What is Helicobacter Pylori and How it affect human health?
-
Table of Contents
“Uncovering the Hidden Danger of Helicobacter Pylori: Protecting Your Health from a Silent Threat.”
Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a type of bacteria that can infect the stomach and small intestine. It is one of the most common bacterial infections in the world, and it is estimated that up to half of the world’s population is infected with H. pylori. H. pylori can cause a variety of gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and bloating. In some cases, H. pylori can also lead to more serious conditions, such as ulcers and gastric cancer. Treatment for H. pylori usually involves a combination of antibiotics and other medications.
What is Helicobacter Pylori and How Does it Affect Human Health?
Helicobacter pylori, commonly known as H. pylori, is a type of bacteria that can infect the stomach and small intestine. It is one of the most common bacterial infections in humans, and is estimated to affect up to half of the world’s population.
H. pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium that is able to survive in the acidic environment of the stomach. It is usually acquired through contaminated food or water, and can be spread through close contact with an infected person.
H. pylori infection can cause a variety of gastrointestinal symptoms, including abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and bloating. In some cases, it can also lead to more serious conditions such as peptic ulcers, gastritis, and even stomach cancer.
The most common treatment for H. pylori infection is a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors. This treatment is usually effective in eliminating the infection, but it is important to note that reinfection is possible.
In conclusion, H. pylori is a common bacterial infection that can cause a variety of gastrointestinal symptoms. It can also lead to more serious conditions such as peptic ulcers and stomach cancer. Treatment with antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors is usually effective in eliminating the infection, but reinfection is possible.
The Link Between Helicobacter Pylori and Gastric Ulcers
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a type of bacteria that is found in the stomach and is associated with the development of gastric ulcers. Gastric ulcers are open sores that form in the lining of the stomach and can cause pain, nausea, and other symptoms.
H. pylori is a spiral-shaped bacterium that is found in the stomach of approximately half of the world’s population. It is believed to be transmitted through contaminated food and water, as well as through contact with an infected person.
The exact role of H. pylori in the development of gastric ulcers is not fully understood. However, it is believed that the bacteria can cause inflammation in the stomach lining, which can lead to the formation of ulcers. H. pylori can also produce toxins that can damage the stomach lining and increase the risk of ulcer formation.
In addition, H. pylori can interfere with the production of stomach acid, which is necessary for proper digestion. This can lead to an imbalance in the stomach’s acidity, which can also increase the risk of ulcer formation.
The diagnosis of H. pylori infection is usually made through a blood test or a breath test. Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics and medications to reduce stomach acid. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the ulcer.
In conclusion, H. pylori is a type of bacteria that is associated with the development of gastric ulcers. It is believed to be transmitted through contaminated food and water, as well as through contact with an infected person. Treatment typically involves a combination of antibiotics and medications to reduce stomach acid.
How to Diagnose and Treat Helicobacter Pylori Infections
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a type of bacteria that can cause infections in the stomach and small intestine. It is estimated that up to two-thirds of the world’s population is infected with H. pylori. While most people do not experience any symptoms, some may experience abdominal pain, nausea, bloating, and loss of appetite. In some cases, H. pylori infections can lead to more serious conditions such as ulcers and even stomach cancer.
Diagnosis of H. pylori infections is typically done through a combination of tests. The most common test is a blood test, which looks for antibodies to the bacteria. Other tests include a stool sample, breath test, and endoscopy.
Once a diagnosis of H. pylori infection is made, treatment is typically done with a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications. The antibiotics used to treat H. pylori infections include amoxicillin, clarithromycin, and metronidazole. Acid-suppressing medications such as proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are also used to reduce the amount of acid in the stomach, which helps to reduce symptoms and promote healing.
In some cases, lifestyle changes may also be recommended. These include avoiding foods that can irritate the stomach, such as spicy or acidic foods, and quitting smoking. Additionally, it is important to maintain good hygiene, as H. pylori can be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces.
It is important to note that H. pylori infections can be difficult to treat and may require multiple rounds of antibiotics and other medications. Additionally, it is important to follow up with your doctor to ensure that the infection has been successfully treated.
In conclusion, H. pylori infections can be diagnosed through a combination of tests and treated with a combination of antibiotics and acid-suppressing medications. In some cases, lifestyle changes may also be recommended. It is important to follow up with your doctor to ensure that the infection has been successfully treated.
Q&A
Q1: What is Helicobacter Pylori?
A1: Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a type of bacteria that can infect the stomach and small intestine. It is one of the most common bacterial infections in humans, and is estimated to affect up to half of the world’s population.
Q2: How does Helicobacter Pylori affect human health?
A2: H. pylori infection can cause a variety of digestive symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and loss of appetite. It can also lead to more serious conditions such as peptic ulcers, gastritis, and even stomach cancer.
Q3: How is Helicobacter Pylori treated?
A3: H. pylori infection is usually treated with a combination of antibiotics and other medications. The exact treatment plan will depend on the individual and the severity of the infection. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and reducing stress can also help to reduce symptoms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Helicobacter pylori is a type of bacteria that can cause a variety of gastrointestinal issues in humans. It is most commonly associated with peptic ulcers, but it can also cause gastritis, stomach cancer, and other digestive problems. While it is not always harmful, it is important to be aware of the potential risks associated with H. pylori and to seek medical attention if any symptoms arise.
A company Etest Medical offers good helicobacter pylori test solution worldwidely.



